Phishing, virtual abuse of trust
Phishing is a type of computer attack that results in an attempt of identity theft. The attacker disguises his action under a seemingly legitimate request such as an email from a bank or a Skype message from a friend. The goal is to fetch the personal data of victims, passwords and login name, to steal his digital assets. Phishing usually acts coarsely, relying on numbers rather than quality. Some recurring factors within these attacks can alert as follows:
- The message is often impersonal.
- The spelling is of poor quality.
- Very sensitive information can be requested (credit card code, passwords…).
- An emergency is mentioned that must be addressed without delay.
- It is always asked to open a link or an attached file.
Although it is less impressive than more sophisticated attacks such as crypto-ransomware, phishing is one of the most common risk vectors. In 2018, the Luxembourg private sector (CERT, CIRCL) recorded more than 6,500 phishing attempts, which accounted for 54.9% of all reported incidents. This trend is particularly related to the simplicity of implementation of the phishing campaign, due to low technical and financial needs. The purchase of a database containing many email addresses is a frequent service on pirate websites.
A constantly evolving threat
Spear phishing is a derived form aimed at a particular person. This technique requires more resources because the attacker must define his message so that it is directly addressed to the victim, which requires retrieval of information upstream. Spear phishing is particularly used in cases of industrial espionage or attacks targeting particularly wealthy people or those holding very sensitive information. Another declination, considered lower tech, is called SMiShing. The malicious intent is similar, but the vector used is a mobile phone or smartphone.
It is not just about your email address!
Like a theft of identity papers, the problem with phishing is to be able to detect where the spoofing stops. Since attackers have recovered your personal information, it is very easy for them to present themselves under your digital identity to different service providers. In addition, the steps to prove your true identity and regain control of these different accounts are long and tedious. It is, therefore, necessary to change your passwords regularly and not to use the same for different services.
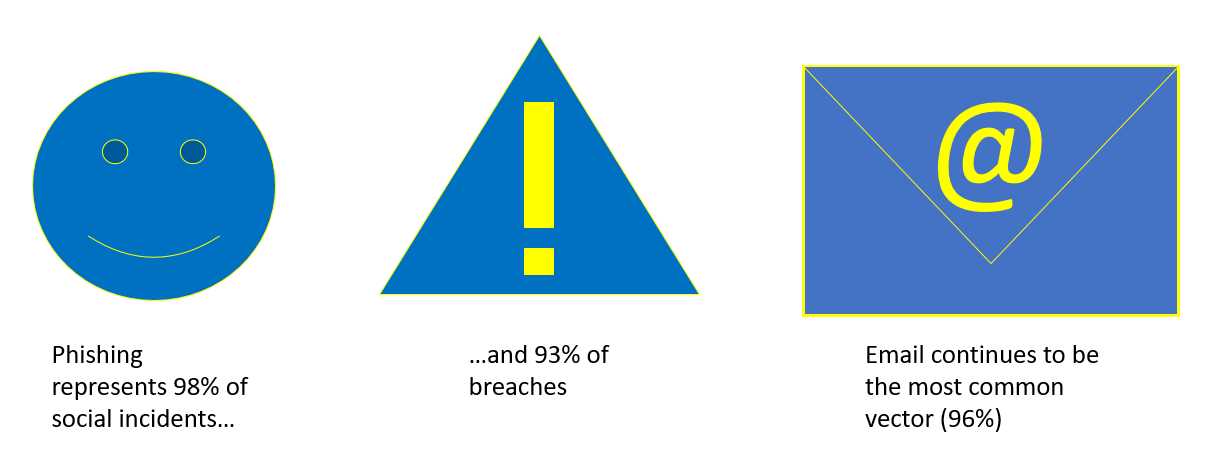
Source: Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report - 2018
To fight against phishing, bet on men as much as on technology
To prevent threats from the phishing campaign, both the right tools and the right practices must be adopted. Among the most accessible tools are anti-phishing filters and proxies which are available by search engines. These are present in the navigation settings of the browsers and do not require any special technical skills (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox…). To supplement these filters, other initiatives should be allowed to report phishing attempts and thus to keep the databases of web browsers up to date. In Luxembourg, the phishing initiative has collected more than 35,000 dangerous URLs since the beginning of the year. The free tool, Web Of Trust, also works via the contributions of its community of users and makes it possible to obtain, or to attribute, a note of trust to the websites visited. However, the use of technical means is not an end in itself and Internet users must adopt a more cautious attitude towards the messages they receive. Employees must be able to take the time to acquire, develop, and practise good reflexes to fight online scams. This may seem like a long time, but one must always take into account possible losses in case of a successful attack and disastrous consequences for the image of the organisation or company. These behaviours can be initiated through training or awareness campaigns, such as this article. NC3 offers training for all types of professional audiences to raise awareness of these issues. Sources of information such as phishing.fr can also allow CISOs, and all employees, to access relevant information that is easily understandable.
NC3 expert voice:
‘Phishing is primarily aimed at humans while exploiting our various weaknesses. In addition to the technical tools mentioned above, here are some tips to prevent leakage of information by phishing:
- Make users aware of the different phishing methods to identify the traps that have been set for them more easily.
- Consider the mails of strangers with extreme caution and attention. If the person is known to us, then s/he must be contacted by other means of communication in case of suspicion of phishing.
- Take a step back to assess the legitimacy of each request.
- Never respond to a phishing email, as this would give the information that the email address is valid.
- In case of doubt, ask the IT staff to ensure the truthfulness of the email you received.’